Brittlebush
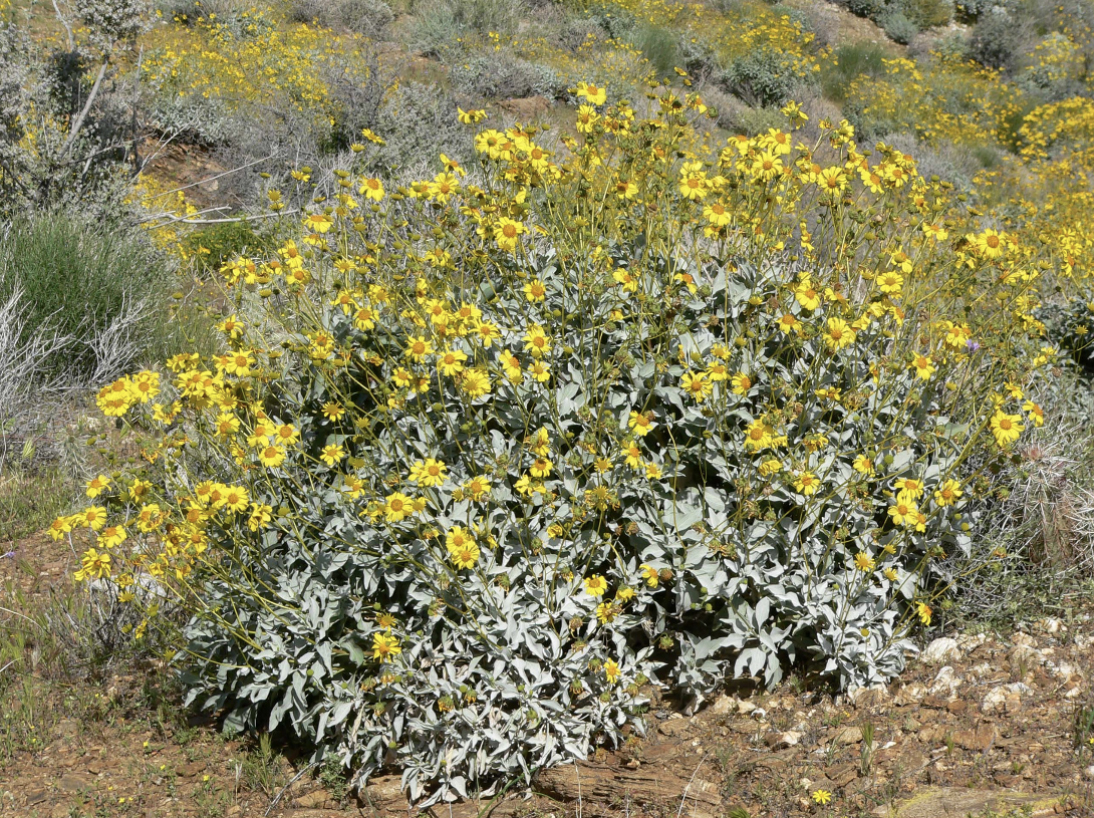

Photo of ''Encelia farinosa'' (brittlebush) in Palm Canyon, California, taken March 2005 by User:Stan Shebs
About
Brittlebush is quite a spectacle! Easy to spot with its bright yellow flowers and silvery green leaves, this perennial plant is incredibly abundant throughout the desert. These medium-sized, rounded shrubs grow to be 2-5 feet tall. They have a deep taproot along with wide, shallow roots. The growth of this plant is dependent on water availability, with most growth occurring during periods of heavy rain, like the summer monsoon season and winter rains the Sonoran Desert receives.
Adaptations
The silvery look of brittlebush leaves is due to small, hair-like structures (a relatively common adaptation among desert plants). These hairs act like a blanket over the leaves to protect them from the heat and cold. The white color reflects the sunlight, helping to keep the plant cool. Additionally, these hairs help trap precious moisture and reduce the amount of water lost.
Food Web
Brittlebush leaves are eaten by bighorn sheep and mule deer, while the seeds are enjoyed by rodents. Brittlebush is drought- and frost-deciduous, meaning that it will drop its leaves during times of extreme drought or cold. During these times, it does not produce food for the aforementioned species.
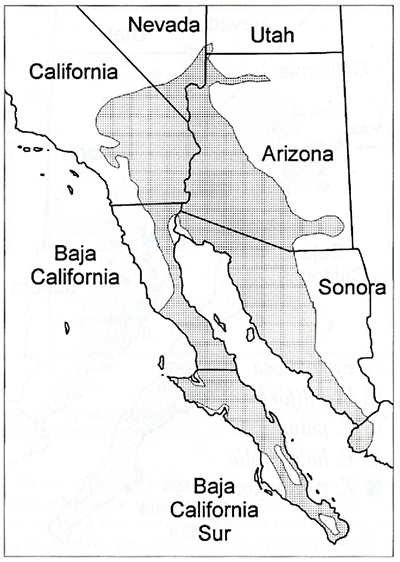
Habitat and Range
Brittlebush can be found in various biomes throughout Arizona, California, Nevada, Utah, and Mexico. It is found throughout the Sonoran Desert and in the warmer areas of the Mojave Desert. It also can be found growing in the coastal chaparral and interior valleys of southern California. It is often the dominant shrub in areas that it inhabits.

Chris English
Family Life
Brittlebush is pollinated primarily by insects. The plant then produces seeds that are dispersed by the wind and tend to sprout after heavy winter rains. They can also sprout clones from the root crown, though this is far less common. Their life span is estimated to be fewer than 20 years.
Glossary
- Root Crown:
- the part of the root system from where a plant stem grows
- Ecological Restoration:
- helping a degraded, damaged, or destroyed ecosystem to recover
- Allelopathic:
- Able to produce chemicals that inhibit the growth and development of other organisms.
Fun Facts
- Brittlebush gets its name for its brittle (easy to break) and woody stems
- Brittlebush is a member of the sunflower family.
- Brittlebush resin has a strong, frankincense-like odor and can be used as incense, hence one of its Spanish names being incienso.
- The sticky sap of this plant can be used as glue, sealant, varnish, and chewing gum.
- This plant has been used medicinally throughout time. Indigenous groups have used it to treat toothache and chest pain.
- Brittlebush is allelopathic, thus allowing it to form dense stands throughout its range.
Conservation
- Brittlebush is abundant throughout its historic range
- This plant is extremely useful for ecological restoration as it helps minimize erosion and is easily grown from seed.
Conservation Index
At The Museum
Pay close attention while you explore — brittlebush can be found amidst the foliage throughout the Desert Museum!